Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a stateless protocol to resolve IP addresses to machine MAC addresses. Every internet network device that needs to communicate on the network broadcast ARP queries in the system to know other devices MAC address. This is know as ARP Poisoning and also known as ARP Spoofing.
In order to learn more about ARP Poisoning, we have used EtterCAP to perform an ARP poisoning attack on LAN environment using Virtual Environment in which we have installed Kali Linux and Ettercap to sniff the local traffic in LAN.
How Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) works
- When a device needs to communicate with other over the internet, it looks up its ARP table.
- If the MAC address isn’t in the table, the ARP_request is broadcasted over the network.
- All the machines on the network will compare this IP address to MAC address.
- If one of the machines in the network identifies this address, then it will respond to the ARP_request with its IP and MAC address.
- The requesting computer will store the address pair in its ARP table and communication will take place.
What is ARP Poisoning or ARP Spoofing?
ARP packets can be forged to send data to the attacker’s machine.
- ARP spoofing constructs a large number of forged ARP request and reply packets to overload the switch.
- The switch is set in forwarding mode and after the ARP table is flooded with spoofed ARP responses, the attackers can sniff all network packets.
Attackers flood a target computer ARP cache with forged entries, which is also known as poisoning. ARP poisoning uses Man-in-the-Middle access to poison the network.
ARP Poisoning and MiTM
The Man-in-the-Middle attack (MiTM) implies an active attack where the adversary impersonates the actual user by creating a connection between the target and sends messages between them. In this way, the victims believes that they are communicating with each other, but in reality, the malicious attacker (man in the middle) controls the communication. Some secure protocols like SSL serve to prevent this type of attack.
In order to get started, you require following tools;
- VMware workstation
- Kali Linux or Linux Operating system
- Ettercap Tool
- LAN connection
Steps to Follow
ARP attack is possible in both wireless and wired networks. You can play this attack in local LAN.
- First of all, install the VMware workstation/ virtualbox on your macine and install the Kali Linux virtual operating system.
- Once the Kali is installed, login to Kali virtual mahcine. Default username and password is root and toor.
- Make sure you’re connected to local LAN and check your IP address by typing the command ifconfig in the terminal.
- Open up the terminal and type Ettercap –G to start the graphical version of Ettercap.
- As graphical interface opens, click on the tab Sniff from the top menu bar and choose unified sniffing and hit OK. We are going to use eth0 which means Ethernet connection.
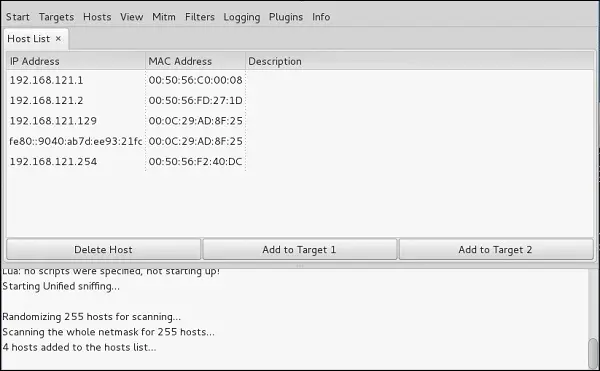
- Click on the Hosts from the top menu bar and click Scan for hosts. It’ll start scanning for the active hosts over the network for all the active hosts.
- Now click on the Hosts and choose Hosts List to see the available number of hosts. It also shows the default gateway IP address. Be careful of selecting the target.
- Next is to choose target. In this virtual MiTM environment, our target is the host machine and the route will be the router address to forward the traffic. In the MITM attack, the attacker intercepts the network and sniffs packets. So, we will add the victim as target 1 and the router address as target 2.
Note: In VMware virtual environment, the default gateway address will always end with 2 because 1 is assigned to the physical machine.
- In this scenario, our target is 192.168.121.129 and the router is 192.168.121.2. So we will add target 1 as victim IP and target 2 as router IP.
- Now click on MiTM and further ARP poisoning. Thereafter, check the option Sniff remote connections and hit OK.
- Click on Start and select Start sniffing. This will start ARP poisoning over the local network which means we have enabled the network card in promiscuous mode and now the local traffic can be captured and sniffed.
Note: Ettercap only sniffs HTTP packets. Secure HTTPS packets can not be sniffed.
- Now if the victim logs into a website. You can see their login details in the Results over the Ettercap toolbar.
This is all how ARP Poisoning works. Hope you understood how easy it is to sniff the non secure HTTP packets over the network with ARP spoofing.
ARP Poisoning has the potential to cause huge damage to corporate company environments. For such attacks and environments, ethical hackers are appointed to secure the networks.
Conclusion
ARP Poisoning, or ARP Spoofing, is a powerful technique used in Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attacks, allowing attackers to intercept and sniff network traffic. By flooding the network with forged ARP packets, attackers can compromise communication between devices, potentially capturing sensitive information. Using tools like Ettercap, anyone can demonstrate this attack in a controlled environment, such as a LAN setup with Kali Linux.
Understanding and testing ARP Poisoning is crucial for cybersecurity professionals to safeguard networks against such threats. Always use this knowledge responsibly and ethically to enhance network security and protect against potential attacks.